Salivary Glands 1
Parotid
This is a slide of parotid gland. This gland is almost 100% serous in nature, with little, if any, evidence of mucous secreting elements. Some secreting elements have been replaced by fat cells. The parotid has the most well developed ductal system of the major glands with prominent striated ducts and numerous intercalated ducts within the secretory lobules and larger collecting ducts found within the connective tissue stroma between the lobules.
The secretory element within the gland
is the serous acinus - a
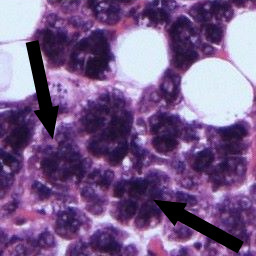 spherical arrangement of cells
with a central collecting lumen and an exit via
a duct (the intercalated duct). The cells are
pyramidal in shape with a basally placed nucleus
and numerous secretory granules apically. These granules stain intensely
and the granular nature of the apical cytoplasm
can be seen at the highest magnification.
spherical arrangement of cells
with a central collecting lumen and an exit via
a duct (the intercalated duct). The cells are
pyramidal in shape with a basally placed nucleus
and numerous secretory granules apically. These granules stain intensely
and the granular nature of the apical cytoplasm
can be seen at the highest magnification.
The intercalated ducts transfer the secreted
saliva from their
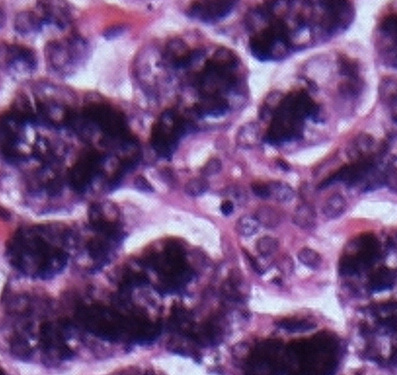 site of production in the acini to the nearest striated duct. They have a
wall of low columnar cells which stain less
intensely than the acinar cells (although some
cells nearest the exit from the acinus may
retain some secretory function). Because of
their small size they may be difficult to spot
in transverse section. When sectioned
longitudinally they may appear as two parallel
line of cells which are stained less intensely
than surrounding acini.
site of production in the acini to the nearest striated duct. They have a
wall of low columnar cells which stain less
intensely than the acinar cells (although some
cells nearest the exit from the acinus may
retain some secretory function). Because of
their small size they may be difficult to spot
in transverse section. When sectioned
longitudinally they may appear as two parallel
line of cells which are stained less intensely
than surrounding acini.
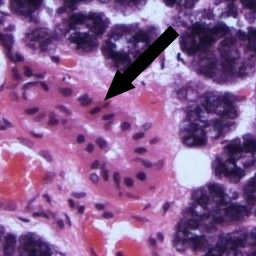 The
striated duct is so called because at high
magnification the basal ends of the cells making
up the wall of the duct are thrown into numerous
folds, giving the outer surface of the duct a
striated appearance. These folds are associated
with numerous mitochondria. The striated duct is
where the main modification of the saliva takes
place due to re-uptake of several salivary
components (Na, Cl) and the addition of others (e.g.
HCO3). This exchange is an active process and
the net result is saliva which is normally
hypotonic.
The
striated duct is so called because at high
magnification the basal ends of the cells making
up the wall of the duct are thrown into numerous
folds, giving the outer surface of the duct a
striated appearance. These folds are associated
with numerous mitochondria. The striated duct is
where the main modification of the saliva takes
place due to re-uptake of several salivary
components (Na, Cl) and the addition of others (e.g.
HCO3). This exchange is an active process and
the net result is saliva which is normally
hypotonic.
To open the e-Scope, click on the demarcated area in the micrograph below:-