Salivary Glands 2
Submandibular
This is a slide of a submandibular gland. It is a mixed gland although the serous element far exceeds the mucous component, possibly by a ratio of as much as 10:1. Striated ducts are prominent as in the parotid (particularly in the serous secreting areas) but intercalated ducts are less in evidence. The mucous secreting elements may be found in recognisable clusters and as individual units dispersed among the serous secreting acini.
The serous acini are similar to those found in the parotid although some of the serous component may be in the form of serous 'demilunes' (see below).
Mucous acini (red
arrow) are a minority of the secretory
elements in the submandibular. They are more
tubular
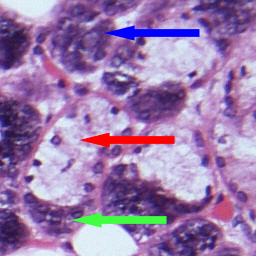 than
the serous acini(blue
arrow) found elsewhere, they stain much
less intensely, containing a pale flocculent
material and do not open into an intercalated
duct (they form their own ductal system within
the parenchyma). They should not be confused
with the clear spaces which are the ghosts of
fat cells. In many mucous acini there is a 'cap'
of serous secreting cells - the so-called serous
'demilune' (green arrow). There is some debate
as to whether the demilune appearance is to some
extent artefact, being produced by the fixation
and embedding process.
than
the serous acini(blue
arrow) found elsewhere, they stain much
less intensely, containing a pale flocculent
material and do not open into an intercalated
duct (they form their own ductal system within
the parenchyma). They should not be confused
with the clear spaces which are the ghosts of
fat cells. In many mucous acini there is a 'cap'
of serous secreting cells - the so-called serous
'demilune' (green arrow). There is some debate
as to whether the demilune appearance is to some
extent artefact, being produced by the fixation
and embedding process.
To open the e-Scope, click on the demarcated area in the micrograph below:-